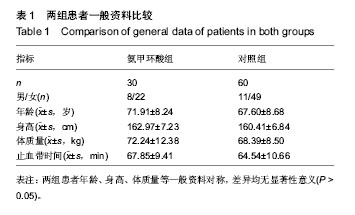
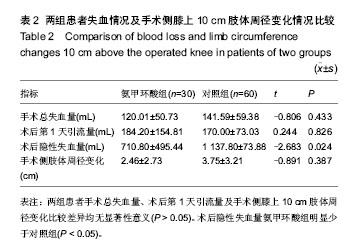
| [1] Ferraris VA, Brown JR, Despotis GJ, et al. 2011 update to the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists blood conservation clinical practice guidelines. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91(3):944-982.
[2] Lemaire R. Strategies for blood management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(9): 1128-1136.
[3] 高福强,李子剑,张克,等.初次全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的影响因素研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2011, 49(5): 419-423.
[4] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2009; 33(5):1263-1268.
[5] Fahmy NR, Patel DG. Hemostatic changes and postoperative deep-vein thrombosis associated with use of a pneumatic tourniquet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981;63(3):461-465.
[6] Nakahara M, Sakahashi H. Effect of application of a tourniquet on bleeding factors in dogs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967;49(7):1345-1351.
[7] Madjdpour C, Spahn DR. Allogeneic red blood cell transfusions: efficacy, risks, alternatives and indications. Br J Anaesth. 2005;95(1):33-42.
[8] Abrishami A, Chung F, Wong J. Topical application of antifibrinolytic drugs for on-pump cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Anaesth. 2009; 56(3):202-212.
[9] Tobias JD. Strategies for minimizing blood loss in orthopedic surgery. Semin Hematol. 2004;41(1 Suppl 1): S145-156.
[10] Sabatini L, Trecci A, Imarisio D, et al. Fibrin tissue dhesive reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. J OrthopTraumatol. 2012;13(3):145-151.
[11] McCormack PL. Tranexamic Acid: a review of its use in the treatment of hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs. 2012;72(5): 585-617.
[12] Ahlberg A, Eriksson O, Kjellman H. Diffusion of tranexamic acid to the joint. Acta Orthop Scand. 1976;47(5): 486-488.
[13] Ker K, Edwards P, Perel P, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding: systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;344:e3054.
[14] Soni A, Saini R, Gulati A, et al. Comparison Between Intravenous and Intra-articular Regimens of Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Blood LossDuring Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014.
[15] Patel JN, Spanyer JM, Smith LS, et al. Comparison of Intravenous versus Topical Tranexamic Acid in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Study. J Arthroplasty. 2014.
[16] Zhou XD, Tao LJ, Li J, et al. Do we really need tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty? A meta?analysis of nineteen randomized controlled trials. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(7):1017-1027.
[17] Raviraj A, Anand A, Chakravarthy M, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a randomized control trial.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;22:381-386.
[18] Gillette BP, DeSimone LJ, Trousdale RT,et al. Low Risk of Thromboembolic Complications With Tranexamic Acid After Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):150-154.
[19] Alshryda S, Sarda P, Sukeik M, et al. Tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(12):1577-1585.
[20] Eubanks JD. Antifibrinolytics in major orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(3):132-138.
[21] Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(13):1153-1159.
[22] Roy SP, Tanki UF, Dutta A,et al. Efficacy of intra-articular tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unilateral totaI knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12):2494-2501.
[23] Sa-Ngasoongsong P, Channoom T, Kawinwonggowit V, et al. Postoperative blood loss reduction in computer-assisted surgery total knee replacement by low dose intra-articular tranexamic acid injection together with 2-hour clamp drain:a prospective triple-blinded randomized controlled trial. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2011;3(2):e12.
[24] Mutsuzaki H, Ikeda K.Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid via drain plus drain-clamping to reduce blood loss in cementless total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 29;7:32.
[25] 高福强,李子剑,张克,等.人工关节置换术后隐性失血计算方法的初步探析[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1144-1145.
[26] Bong MR, Patel V, Chang E, et al. Risks associated with blood transfusion after total keen arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004,19(3):281-287.
[27] 孙伟,李子荣.人工关节置换术围手术期的血液管理[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(4):244-247.
[28] Spahn DR, Casutt M. Eliminating blood transfusions: new aspects and perspective Anesthesiology. 2000;93(1): 242-255.
[29] Etchason J, Petz L, Keeler E, et al. The cost effectiveness of preoperative autologous blood donations. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332(11):719-724.
[30] Rama KR, Apsingi S, Poovali S, et al. Timing of tourniquet releasc in knee arthmplasty.Meta-analysis of randomized,controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):699-705.
[31] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(5):1263-1268.
[32] Ishida K, Tsumura N, Kitagawa A, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(11):1639-1645.
[33] Craik JD, Ei Shafie SA, Kidd AG,et al. Can local administration of tranexamic acid during total knee arthroplasty reduce blood loss and transfusion requirements in the absence of surgical drains? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(3):379-384.
[34] Seo JG, Moon YW, Park SH, et al. The comparative efficacies of intra-articular and IV tranexamic acid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1869-1874.
[35] Alshryda S, Mason J, Vaghela M, et al. Topical (intra-articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total kneereplacement: a randomized controlled trial (TRANX-K). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21):1961-1968.
[36] Kim TK, Chang CB, Koh IJ. Practical issues for the use of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013.
[37] Wong J, Abrishami A, El Beheiry H, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15):2503-2513.
[38] 马云青,张轶超,张洪.氨甲环酸在单侧全膝关节置换术中局部应用的止血效果分析[J].中华外科杂志, 2013, 51(1): 40-43.
[39] Sa-ngasoongsong P, Wongsak S, Chanplakorn P, et al. Efficacy of low-dose intra-articular tranexamic acid in total knee replacement; a prospective triple-blinded randomized controlled trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14(1): 340.
[40] MacDessi S, Chen D. Dose-Dependent Effects of Intra-Articular Injection of Tranexamic Acid on Bleeding in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bone Joint J Orthop Proceeding. 2013;95(Supp 15): 34-34. |